Advanced Imaging for Accurate Diagnosis
CT Scan
Currently MRI & CT Scans are not available due to technical problems that are being processed.
Zia Vet Clinic is one of the only clinics in Pakistan that facilitates sophisticated imaging procedures such as MRI & CT scan, allowing greater access to advanced diagnostic tools for your pets. The high-resolution results produced offer a very detailed picture allowing us to follow the image slices sequentially to get a very comprehensive understanding of your pet’s internal health. These results can also be used to reconstruct a 3-D image of the concerned area providing vital information needed to plan for surgery. Our clinic often serves as a referral clinic to make use of such complex diagnostic results. These results allow us to assess all parts of the body for potential cancer checks, bone defects/fractures, nerve injury, ear disease, spinal injuries, and other such complicated health issues in pets.
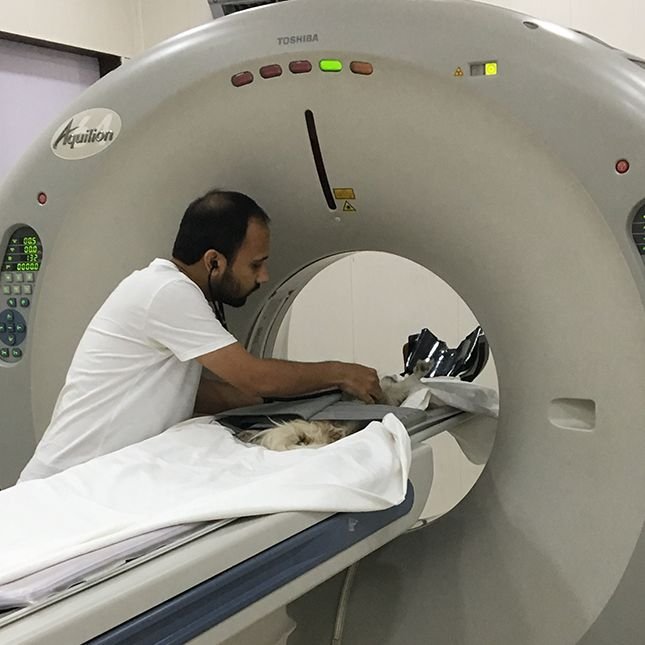
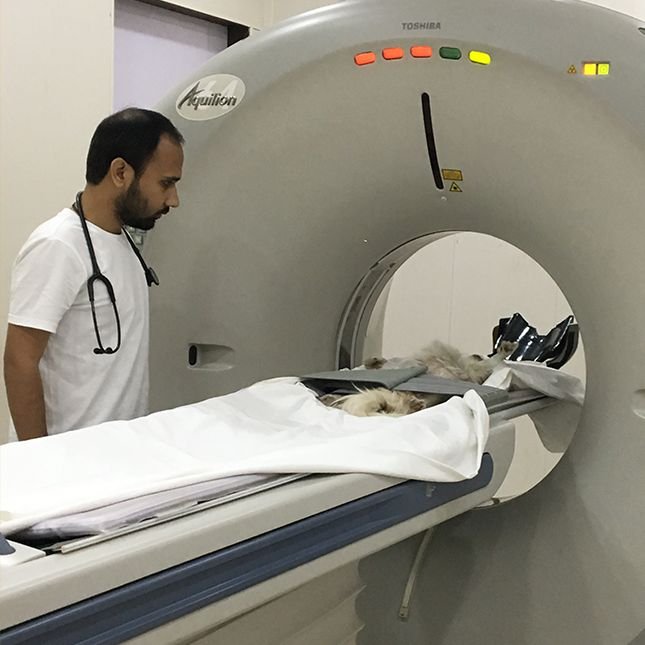
CT
Computed Tomography (CT) imaging uses X-rays in conjunction with digital X-ray detectors and computer processors to image the patient. A CT scan is sometimes called a CAT scan (for computed axial tomography).
For a CT scan, a dog or cat is placed under anesthesia, positioned on a table that slides the pet through a ring containing the x-ray source and the X-ray detectors. The CT images are cross-sectional slices of the area imaged, as if the patient was cut like a loaf of bread. These slices can be examined one by one to reveal the details inside.
Contrast agents containing iodine are typically administered intravenously as part of the scanning process to enhance visualization of abnormal soft tissues and blood vessels. VRIC uses a helical / spiral scanner to rapidly acquire images of dogs, cats and exotic animals. General anesthesia is typically used because most studies require the patient to remain motionless for a few minutes.
A CT scan can take a few minutes to an hour depending on the complexity of the exam, the size of the patient, and the number of body regions examined.
After the CT scan is acquired and the patient is awake, CT images can be further processed and reconstructed into two-dimensional and three-dimensional images using computer manipulation for further analysis as radiologists evaluate the images.
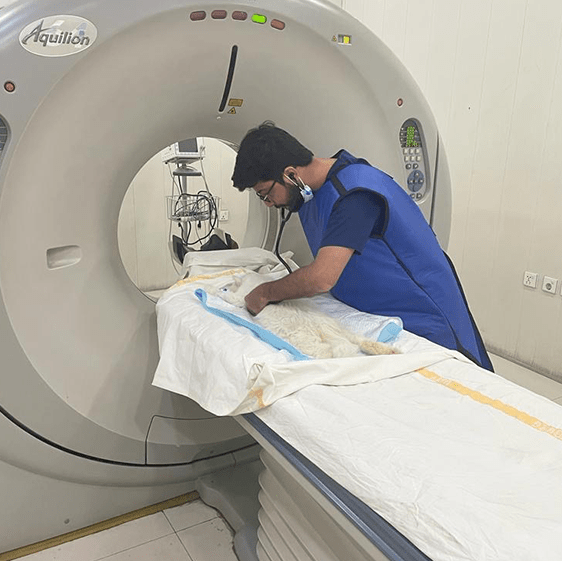
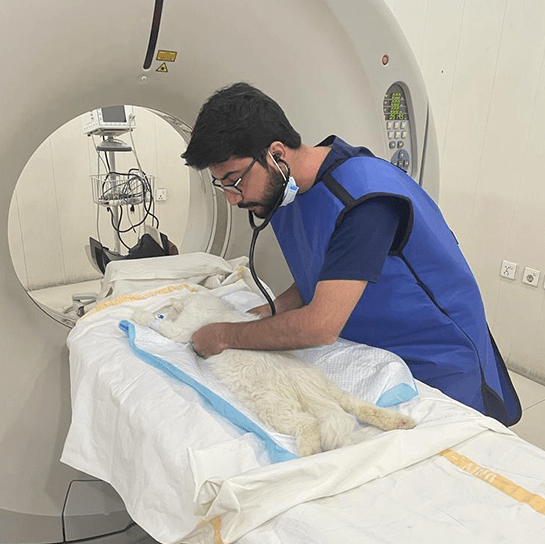
CT Scans For Dogs
Boca Park Animal Hospital is one of only two animal hosptials in the Las Vegas Valley to have a CT scanner on site.
CT scans for dogs, also known as ‘cat scans’, are computer enhanced dog x-ray procedures most often used to evaluate complex parts of the body, such as the head, chest, some joints and various internal organs. CT scans show different levels of tissue density, and produce more detailed images than x-rays. Unlike MRI’s, CT scans for dogs do not use magnetic field waves so they cannot compare changes in fluid levels due to inflammation or bleeding. Therefore, CT scans for dogs are used in situations where an MRI is considered unnecessary but a traditional x-ray is inconclusive or insufficient.
CT scans for dogs usually proceed as follows:
- Dogs must be sedated for this procedure because they cannot be restrained by humans and must remain still during the procedure
- The dog is placed on a motorized bed inside of a CT scanner, a machine that takes a series of x-rays from various angles.
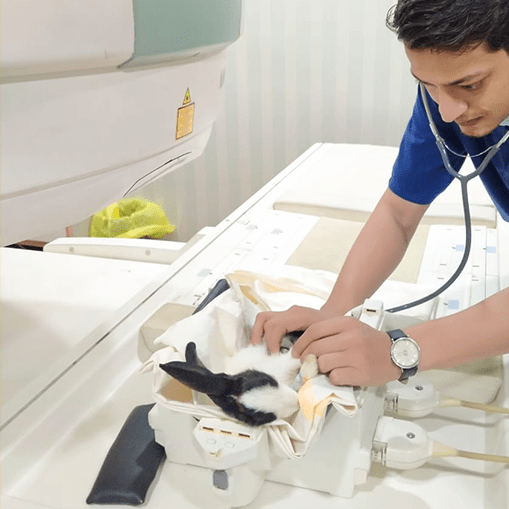

MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI, is the newest form of diagnostic imaging being used for both human and veterinary medicine. Dog MRI equipment generates a very powerful magnetic field, resulting in detailed anatomic images of whatever part of a dog’s body is being scanned. No x-rays are involved, and a dog MRI is considered extremely safe.
A dog MRI procedure usually proceeds as follows:
- Dogs must be sedated for this procedure because they cannot be restrained by humans and must remain still during the procedure
- For the procedure, a dog is placed in a tubular electromagnetic chamber
- The dog’s body is continuously pulsed with radio waves for a period of time, usually 10-20 minutes
- The pulsing causes the dog’s body tissues to emit radio frequency waves that can be detected by the MRI equipment. Many repetitions of these pulses and subsequent emissions are required in order to generate adequate digital feedback for the equipment to interpret
- The feedback is then converted into images that can be displayed on a screen, and can also be saved for future study

JT Lahore
- 24-F, Main Boulevard Khayaban-E- Firdosi, Johar Town, Lahore, Pakistan.
- +924235220750
- VIEW ON MAP

DHA Karachi
- 61-C , Zulfiqar Commercial Avenue , Phase - VIII , DHA Karachi, Pakistan.
- +923139999759
- VIEW ON MAP

